Don't have an account?
Creating an account has many benefits: check out faster, keep more than one address, track orders and more.
Or
Checkout as a Guest
Place your order without creating an account for extra convenience.
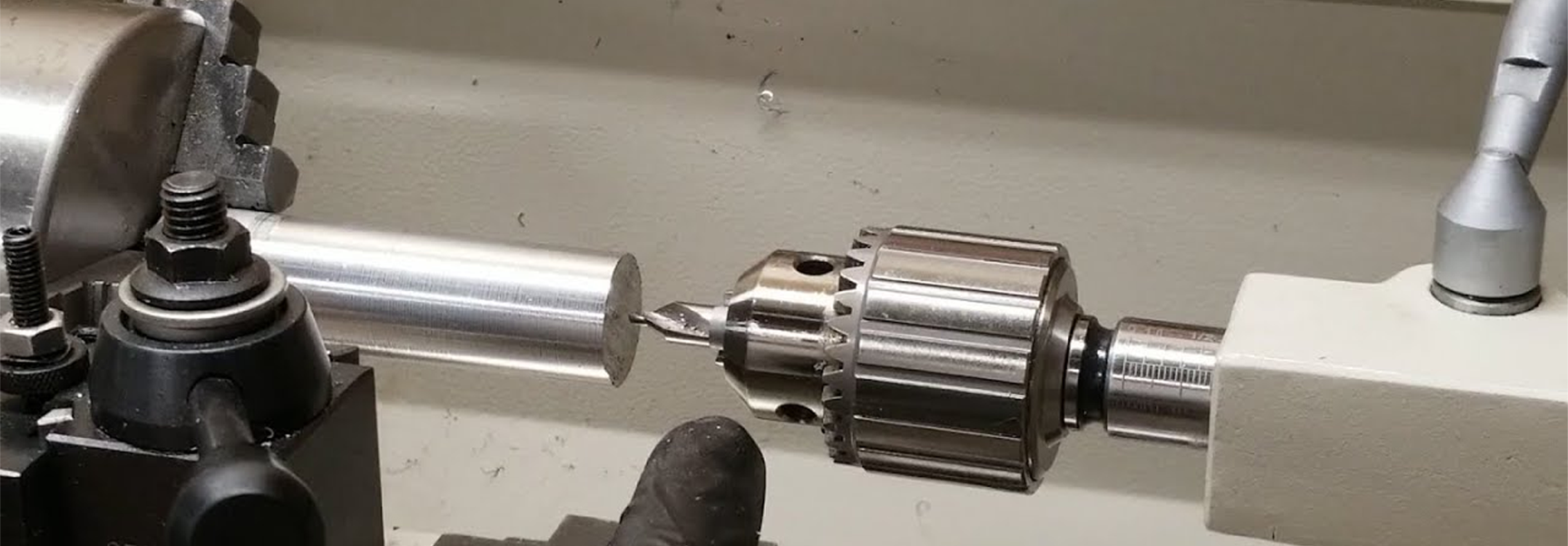
An Expert Guide on Centre Drills
Contents
There are lots of things to consider when looking to purchase the right centre drill for your application.
When it comes to centre drills, they are primary tools in precision machining, offering distinct advantages across various applications. This blog explores the basics of centre drills, detailing their key features and benefits. It also provides practical guidance on how to choose and use centre drills effectively.
Whether you're new to machining or looking to improve your technique, this guide will help you understand the role of centre drills and how to optimise them for your machining needs.
What Are Centre Drills?
Centre drills are essential tools in precision machining, designed specifically to create small, accurate holes at the end of a workpiece. These holes, known as "centres," serve as guides for larger drills or as support points for live or dead centres in lathe operations. The unique geometry of centre drills, with their shorter, sturdy structure and tapered ends, allows them to withstand greater pressure compared to spot drills, making them ideal for ensuring precise alignment and preventing drill wander.
Centre drills are typically available in High-Speed Steel (HSS) or carbide and come in various sizes. They are also available in two common types: Type A (DIN 333-A) with a 60-degree chamfer, and Type B (DIN 333-B), which features both a 60-degree front chamfer and a secondary 120-degree chamfer. These drills are commonly offered in both Metric and British Standard Imperial sizes, making them versatile tools for a wide range of applications.
In addition to their primary use of creating centres, these drills can also be used as countersinks, allowing countersunk screws to sit evenly with the workpiece surface. Their versatility and robust design make centre drills essential for any task requiring precision and accuracy.
Why Use a Centre Drill?
A centre drill, available in HSS or carbide, is ideal for creating starter or guide holes in various materials, including cast iron, aluminium, copper, steel, and stainless steel. Its short and stubby design helps to prevent deflection, making it perfect for pre-drilling applications. When preparing a hole for a lathe centre, precision is crucial, as it ensures the workpiece stays aligned and stable during machining.
The primary purpose of a centre drill is to create an accurate starting point for drilling or to prepare the workpiece for turning between centres. Using a centre drill ensures that the following operations are performed with the highest precision. Here are the key benefits:
• Supports the Workpiece: Centre drilled holes serve as a reference point for work holding tools, which helps support and stabilise the workpiece in a lathe.
• Creates a Starting Point: Centre drills establish a starting point for larger holes, reducing the risk of the drill bit wandering and preventing deflection.
• Countersinks Holes: Centre drills can also be used to create countersunk holes, allowing fasteners to sit flush with the surface for a cleaner finish.
• Accuracy: Centre drills provide a precise starting point for larger drills, ensuring the final hole is accurately located.
• Enhances Tool Life: Starting with a centre drill reduces the load on subsequent drills, prolonging their life by preventing excessive wear and tear.
HSS vs Carbide Centre Drills
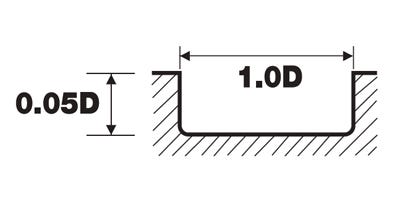
Centre drills are available in High-Speed Steel (HSS) and carbide, each with its own advantages and disadvantages depending on the application.
High-Speed Steel (HSS) Centre Drills
Advantages:
• Cost-Effective: HSS centre drills are more affordable and suitable for general-purpose machining.
• Durability: They offer good durability and are less likely to chip or break under pressure, making them ideal for less rigid setups.
• Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials, including mild steel, aluminium, and plastics.
Disadvantages:
• Lower Hardness: HSS has lower hardness compared to carbide, which can lead to shorter tool life in more demanding applications.
• Limited Speed and Feed Rates: Less efficient in high-speed machining scenarios.
Carbide Spot Drills
Advantages:
• High Hardness: Carbide centre drills offer superior hardness, resulting in extended tool life and improved wear resistance, particularly in hard or abrasive
materials.
• High-Speed Machining: They perform exceptionally well in high-speed applications, enhancing overall machining efficiency.
• Heat Resistance: Carbide retains its hardness at high temperatures, making it suitable for high-speed and high-temperature operations.
Disadvantages:
• Cost: Generally, more expensive, representing a higher initial investment.
• Brittleness: More prone to chipping or breakage under unstable conditions
Overall High-Speed Steel (HSS) centre drills are cost-effective, tough, and versatile, making them ideal for general-purpose machining across various materials. However, they have lower hardness and are less efficient in high-speed operations compared to carbide drills.
Carbide centre drills, on the other hand, offer superior hardness, wear resistance, and performance in high-speed and high-temperature conditions. While they are more expensive and prone to brittleness, they excel in demanding machining tasks and maintain their properties under intense conditions.
What are the different forms and angles available for centre drills?

Centre drills come in various forms and angles, each tailored to specific machining needs.
From A centre drills create a centre hole with a single 60-degree chamfer. They are best suited for forming 60-degree pilot holes in a workpiece, which are ideal for locating a live centre accurately.
Form B centre drills form a hole with two chamfers: a 60-degree chamfer and an additional 120-degree chamfer at the start of the hole. The 120-degree chamfer serves to protect the hole's entrance from damage and deformation, which helps maintain precise centring of the tailstock centre.
Form R centre drills feature a radius instead of a chamfer. This design improves holding accuracy by forming a centre hole with a radius, although it may reduce the load-bearing capacity of the hole.
Form W is designed with a 60-degree point angle but with a longer and more pointed tip, making it useful for deeper centre holes or applications requiring extended reach and better precision.
The angles of centre drills are also designed to meet various specific needs. The 60-degree point angle is the most common and is used for general-purpose centre drilling, providing a sharp and accurate centre hole. The 90-degree point angle is used for larger centre holes or applications where a wider angle is needed for better alignment and stability.
The helix angle can be either straight, offering straightforward cutting action for general tasks, or spiral, which enhances chip removal and overall drilling efficiency. Each form and angle is designed to address specific machining requirements, ensuring that machinists can select the most suitable tool for their needs.
aaa


Coated vs Uncoated Centre Drills
Coated and uncoated centre drills serve similar functions in drilling operations, but their properties and performance can differ significantly due to their coatings.
Coated Centre Drills:
1. Enhanced Durability: Coatings such as titanium nitride (TiN) or carbide improve the drill’s resistance to wear and heat, extending tool life.
2. Better Performance: Coatings can reduce friction and enhance cutting efficiency, allowing for faster drilling and cleaner holes.
3. Reduced Chip Build-up: Coated drills are less likely to suffer from chip weld and material build-up, which helps maintain precision.
Uncoated Centre Drills:
1. Cost-Effective: Generally, less expensive than coated drills due to the lack of additional coating processes.
2. Good for Softer Materials: Effective for drilling softer metals and materials where high wear resistance is not as critical.
3. Simpler Maintenance: No coating means there’s no need to worry about coating wear or degradation.
4. Better for Non-Ferrous Applications: Uncoated tools prove better for non-ferrous materials, as there's no risk of coating build-up on the tool.
Ultimately, coated centre drills offer superior durability and performance, especially for harder materials and challenging applications, while uncoated centre drills are more cost-effective and suitable for less challenging tasks.
aaa


Selecting the Right Centre Drill
When purchasing a centre drill for your application, several key factors should be considered:
• Material Compatibility: Determine the type of material you’ll be drilling—metals, plastics, or composites. Choose a centre drill designed specifically for your material to ensure optimal performance.
• Size and Diameter: Centre drills come in various sizes and diameters. Select a drill that matches the diameter of the hole you need, considering both the pilot hole and countersink sizes if applicable.
• Point Angle: The point angle of the centre drill, typically 60° or 90°, affects its performance. Choose the angle that best fits the requirements of your project.
• Flute Design: Flutes assist with chip removal during drilling. Evaluate the flute design, such as straight or spiral flutes, based on the material being drilled.
• Shank Type: Centre drills are available with different shank types, including straight shank and Morse taper shank. Ensure that the shank type is compatible with your machine or chuck.
• Coating: Coatings like TiN, TiAlN, or TiCN enhance tool durability and reduce friction. Choose a coated centre drill for extended tool life and better
performance.
• Cutting Speeds and Feed Rates: Be aware of the recommended cutting speeds and feed rates for your centre drill, as these parameters influence both performance and tool longevity.
Tips for Using Centre Drills
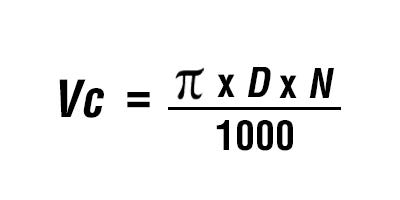
To achieve the best results with centre drills, consider the following:
Proper Setup: Ensure the workpiece is securely clamped, and the machine is set up correctly to avoid vibrations that could affect the accuracy of the centre hole.
Correct Speed and Feed: Use appropriate speed and feed settings based on the material and drill type to maximise tool life and precision.
Alignment: Double-check the alignment of the drill to the workpiece to ensure the centre hole is precisely located.
Lubrication: Use proper lubrication to reduce heat and friction, particularly when drilling hard materials.
What Toolholder to Use for Centre Drills
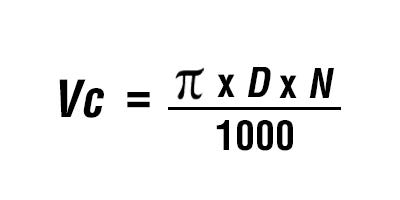
For centre drills, the choice of toolholder is crucial to ensuring precision and stability during operation. ER Collet Chucks, particularly those with Morse taper back ends or straight shanks, are highly recommended due to their ability to provide a secure and precise grip on the drill. This minimises runout and vibration, leading to more accurate and consistent results. Additionally, drill chucks can also be a suitable choice, offering flexibility and ease of use.
The versatility of ER collet chucks also allows them to accommodate a wide range of tool shank sizes, making them a convenient and flexible option for various machining setups. Cutwel offers the largest range of ER collet chucks, with options to suit almost every taper, nut style, and length, ensuring you can find the perfect toolholder for your specific needs.
More uncommonly, centre drills can be supplied with Weldon (flat) shanks. These are more suited to being held in straight shank end mill holders – with the added benefit of more secure clamping to prevent the tool from slipping in the holder.
Centre drills are essential tools for precision machining, providing accurate starting points for drilling and supporting workpieces in lathe operations. By understanding the different types of centre drills, their materials, and coatings, and by following best practices for their use, you can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of your machining projects.
For expert advice on selecting the right centre drill for your application, please contact our technical team on 01924 869 615 or email sales@cutwel.net

